Get Your Free Accessibility & Inclusion Toolkit
Download NowAssistive technology is one of the marvels of the modern world. It represents a transformative approach to inclusion, where devices, systems, and software are used to support individuals with disabilities, making their lives easier, more independent, and more fulfilling. This article delves into the nitty gritty of assistive technology, bringing to the forefront some of its key benefits and examples.
What is Assistive Technology?
Assistive technology is an umbrella term that refers to any device or system designed to help individuals with disabilities perform functions they might otherwise find difficult. Devices available on the market range from mobility aids, like crutches and wheelchairs, to more digital solutions, like screen readers or software.
Though similar in many cases, each technology caters for a different disability. Recite Me’s accessibility toolbar, for example, helps make websites more accessible to users with visual impairments, whilst speech-generating devices (SDGs) provide support for non-verbal individuals.
But regardless of the type of aid or its level of sophistication, the goal of assistive technology is always the same: to increase, maintain, or improve the functional capabilities of individuals with disabilities, so that they can participate more wholly in all aspects of life.

Who does Assistive Technology Benefit?
Assistive technology was designed with disabled individuals in mind. It provides essential tools that help break down barriers to inclusion so that they are not held back from achieving their full potential. A screen reader is an example of high-tech assistive technology that can benefit people with visual impairments by allowing them to digest website content in a way that would not be possible without the technology.
But assistive technology is not selective with who it benefits, making it an attractive prospect for a broad spectrum of society, not just those with disabilities. Employers, for one, see assistive technology as a means of diversifying their talent pool. By integrating tools, like Recite Me’s Accessibility Toolbar, on their websites, employers open the proverbial door to job applications from non-english speakers or those with visual impairments, tapping into broader talent pools as a result.
Educational institutions also benefit from the frills of assistive technology since it allows schools and universities to offer more inclusive, and thus more effective, learning environments, in which all students have equal opportunities to succeed.
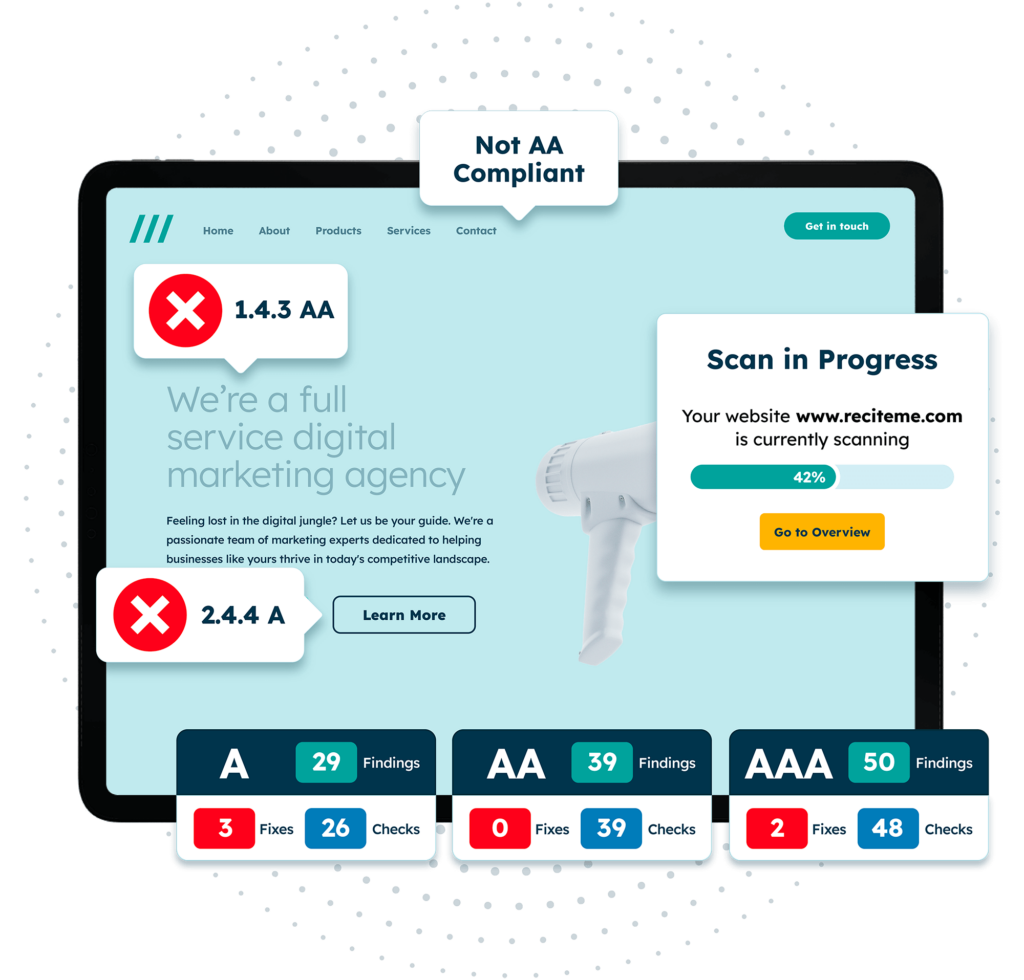
Free Accessibility Check of your Website
Finding accessibility issues is now easier than ever. Recite Me offers a free automated scan of your website’s homepage to highlight non-compliance. You’ll get recommendations on how to fix them, helping to improve your accessibility score.
What are the Benefits of Assistive Technology
Benefits for People with Disabilities
People with disabilities are the most obvious beneficiaries of assistive technology. As a result, there are seemingly endless benefits linked to these devices and systems. Some of the most significant have been outlined below:
- Increased Independence: Assistive technology enables individuals to perform daily tasks without relying on others, giving them a sense of autonomy and self-reliance.
- Improved Communication: Speech-generating tools or text-to-speech software, much like Recite Me’s screen reader toolbar feature, tend to facilitate better communication for those with speech or language impairments. Having digital content read aloud, for example, can help them interpret website information that would have otherwise been rendered inaccessible. These sorts of features play a critical role in the back and forth communication between organisations and those with impairments.
- Enhanced Learning: Tools like audiobooks and specialised educational apps help students with disabilities, such as dyslexia, grasp and retain information more effectively.
- Better Mobility: Wheelchairs, scooters, and other mobility aids offer freedom of movement, meaning individuals with physical disabilities are not prevented from engaging in their desired activities.
- Access to Information: Screen readers, magnifiers, and braille displays provide access to digital and printed information, making it easier to stay informed and connected.
- Increased Employment Opportunities: Job seekers with disabilities can leverage assistive technologies to perform job functions efficiently, opening up more employment possibilities. For instance, hearing aids can facilitate verbal exchanges with clients and colleagues, allowing people with hearing impairments to apply for jobs which depend highly on verbal communication.
Benefits for Organisations and Employers
By leveraging assistive technologies on their websites and in their work environments, employers open themselves up to a whole host of business benefits. Outlined below are some of the most prevalent.
- Diverse Talent Pools: By accommodating employees with disabilities, organisations can access a broader range of skills and perspectives. A company that adopts accessible software can hire talented developers who are visually impaired, enriching their technical team with diverse expertise.
- Enhanced Productivity: Assistive technology can help employees work more efficiently, leading to increased productivity and job satisfaction. The use of tools like ergonomic keyboards designed for accessibility and speech recognition software enable employees with physical disabilities to perform tasks more swiftly and accurately.
- Compliance and Inclusion: An organisation that provides accessible communication tools ensures compliance with disability rights legislation while fostering an environment where all employees feel valued and respected.
- Innovation and Creativity: Employers can use assistive technologies to remove barriers to participation. By including employees with different abilities in brainstorming sessions, for example, companies are more likely to develop products and services that cater to a wider audience, enhancing their market competitiveness.

Benefits for Educational Institutions
Educational institutions benefit from assistive technology too. As schools and universities have a lot to gain from incorporating these technologies into their day to day operations. A list of some of the most common benefits are outlined below.
- Inclusive Learning Environments: Assistive technology ensures that all students, regardless of their abilities, can participate fully in classroom activities, meaning no one is left behind. As a result, schools, universities, and colleges become more attractive to prospective talents.
- Enhanced Learning Outcomes: By providing tailored support, assistive technology helps otherwise disadvantaged students achieve better academic results. For instance, specialised educational apps that use gamification to incentivise productivity could help students with ADHD improve focus. If similar initiatives are employed across the board, this can quickly lead to higher grades and academic success.
- Equal Opportunity: Ensuring access to assistive technology helps bridge the gap between students with and without disabilities, cultivating a more equal educational landscape. A school that provides braille displays and screen readers ensures that blind students have the same access to information as their sighted peers. In doing so, they level the playing field such that no student is made to start their educational journey at a disadvantage. Creating a more diverse and inclusive educational environment.
Benefits for Soceity
- Social Inclusion: Assistive technology promotes the active participation of individuals with disabilities in community activities; an essential part of social cohesion. Mobility aids for example, like electric scooters or wheelchairs, allow individuals with physical disabilities to navigate public spaces independently, participating more fully in community events and social gatherings.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: By providing disabled people the tools to be able to better care for themselves, it reduces the need for medical supervision, and thus, leads indirectly to greater healthcare savings. Devices like home monitoring systems, for example, allow individuals with chronic conditions to detect health issues early on, reducing emergency room visits and hospital stays.
- Improved Quality of Life: Assistive technology enhances the quality of life for individuals with disabilities by providing them with tools to navigate daily challenges more effectively. For instance, speech-generating devices enable non-verbal users to express themselves, communicate with their loved ones, and maintain meaningful relationships. This doesn’t just benefit the user of the assistive technology, but enriches the lives of their family, friends, and those around them too; fostering a general sense of well-being and happiness in the community.
Our 40-page Digital Accessibility & Inclusion Toolkit helps businesses break down online barriers and make a real impact. It offers practical advice on all aspects of digital accessibility, from writing an accessibility statement to accessible website tips and inclusive hiring.

Examples of Assistive Technologies
Assistive technology encompasses a broad range of devices, tools, and applications designed to aid individuals with disabilities in performing tasks that might otherwise be difficult or impossible. Here are some examples of assistive technologies:
Visual Aids
Visual aids are assistive tools that support individuals with low vision or blindness. Very often they refer to digital technologies, like screen readers, magnifiers, or even braille displays. But regardless of the type, all visual aids serve the same purpose: to facilitate interactions between its user and displays of visual content.
Screen readers, for example, convert on-screen text into audible spoken language. For someone who is visually impaired, this gives them the opportunity to navigate digital content without any accessibility barriers. They might choose to use the screen reader to sift through research materials for a school project, or to assist them in the job application process.
Visual aids offer an incredibly versatile range of applications as well as benefits, among them: increased independence, improved learning capabilities, and greater access to information. Because of this, individuals with visual impairments face less challenges in their daily activities and are given the confidence to reach their full potential in life.

Hearing Aids
Hearing aids amplify sounds, enhancing the ability of those with hearing impairments to converse with others, listen to music, and engage with other crucial auditory cues. In social gatherings or work meetings, hearing aids ensure the user correctly understands the information being presented to them. As a result, verbal exchanges are had with clarity and without ambiguity, allowing users to develop more meaningful connections with those around them.
Hearing aids can even be used to enhance shows and other auditory experiences that take place in public spaces, such as theatres and lecture halls, so that individuals with hearing impairments can participate fully in life’s joys without any barriers.
You can learn more about the benefits of assistive technology for people with hearing difficulties here.
Communication Devices
Assistive technology communication devices are designed to assist individuals with speech or language impairments in expressing themselves effectively. Speech-Generating Devices (SGDs), for example, convert user inputs into spoken language, which allows non-verbal individuals to convey thoughts, share ideas, and express opinions. SGDs play a crucial role in many facets of society, but particularly educational settings where verbal interactions between students and teachers are critical to learning.
Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) Apps are another example of communication devices. When installed on tablets or smartphones, they provide a means of communicating through symbols or text-based systems, which is particularly useful for people with conditions like aphasia.
Text-to-Speech Software works in a similar way to Recite Me’s screen reader feature. It converts written on-screen text into verbal speech, allowing messages to be conveyed clearly during situations like presentations where verbal delivery is key.
More than anything though, these devices tear down communication barriers and facilitate everyday interactions for those living with speech or language impairments. Not so dissimilar from hearing aids, they ease social exchanges and help disabled individuals reach their full potential, both in and out of the workplace.
Learning Tools
Learning tools are a type of assistive technology that relate specifically to overcoming education-related barriers. By offering written information in an audible format or presenting resources digitally, things like audiobooks and eBooks allow students with reading impairments to access the materials they need for school or university.
Speech-to-Text Software is a learning tool that is often used by students with writing difficulties to complete assignments by converting their spoken words into written text. Similarly, specialised educational apps, another learning tool, target specific learning needs, such as literacy improvement or mathematical skills development, supporting students with disabilities in achieving academic success by adapting to their unique learning styles.
Ultimately, learning tools play a crucial role in levelling the playing field for students with disabilities, ensuring they have access to all the same resources as their peers. This can benefit students of all ages and levels, including those in special education settings.

Mobility Aids
Mobility aids empower individuals with physical disabilities to navigate their environments with greater independence and confidence. Aids like wheelchairs give them the freedom to go to the shops, visit cities, or travel between spaces without needing support from others. Mobility scooters offer a convenient alternative for longer distances, adding an additional layer of comfort and ease to weekend outings or long commutes.
Other mobility aids like walkers, canes, and crutches, provide stability for those with balance issues. It gives them a means of travelling and performing daily tasks safely; something that many of us take for granted.

Add Assistive Technologies to your Website with Recite Me
Want to leverage the many benefits of assistive technologies? Then make a start today with the Recite Me assistive toolbar, which integrates with your website and offers a variety of assistive tools. With tools including text-to-speech, magnifier, contrast changer, translation software and much more.
- Contact our team for more advice on assistive technology.
- Find out more about the Recite Me Assistive Toolbar.
- Schedule a free demonstration of how our assistive toolbar can help you.
- Run a free scan of your website for WCAG 2.1 AA compliance.



