Get Your Free Accessibility & Inclusion Toolkit
Download NowSoftware-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms power much of the online world, from project management tools to customer relationship management systems, online education platforms, and more. But while SaaS has transformed availability of services, many platforms still fall short in terms of usability for people with disabilities.
Accessibility in SaaS means designing and developing software so that it can be used effectively by everyone, including individuals with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments.
Understanding Accessibility in SaaS
SaaS is a model where software is delivered over the internet, usually through a web browser, instead of being installed directly on a computer. Think of tools like Google Workspace, Zoom, or Salesforce, where users log in online, access the service from anywhere, and the provider manages updates, storage, and security in the background.
But while SaaS removes many traditional barriers (like expensive hardware or complex installations) it can unintentionally create new ones if accessibility isn’t prioritised. When SaaS platforms are not accessible, disabled users may be unable to log in, complete forms, use dashboards, or fully benefit from the service. Considering that over 1 billion people globally live with some form of disability, ignoring accessibility excludes a massive portion of potential users.

The role of WCAG and regional accessibility laws
Accessibility is guided by global standards and reinforced by regional legislation. The most widely recognised framework is the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), developed by the W3C. WCAG provides criteria at three levels: A (basic), AA (mid-level, widely adopted), and AAA (the highest).

In addition to WCAG, there are also regional laws govern accessibility:
SaaS providers serving global audiences must be aware of these frameworks, as failure to comply can lead to lawsuits, fines, or market exclusion.
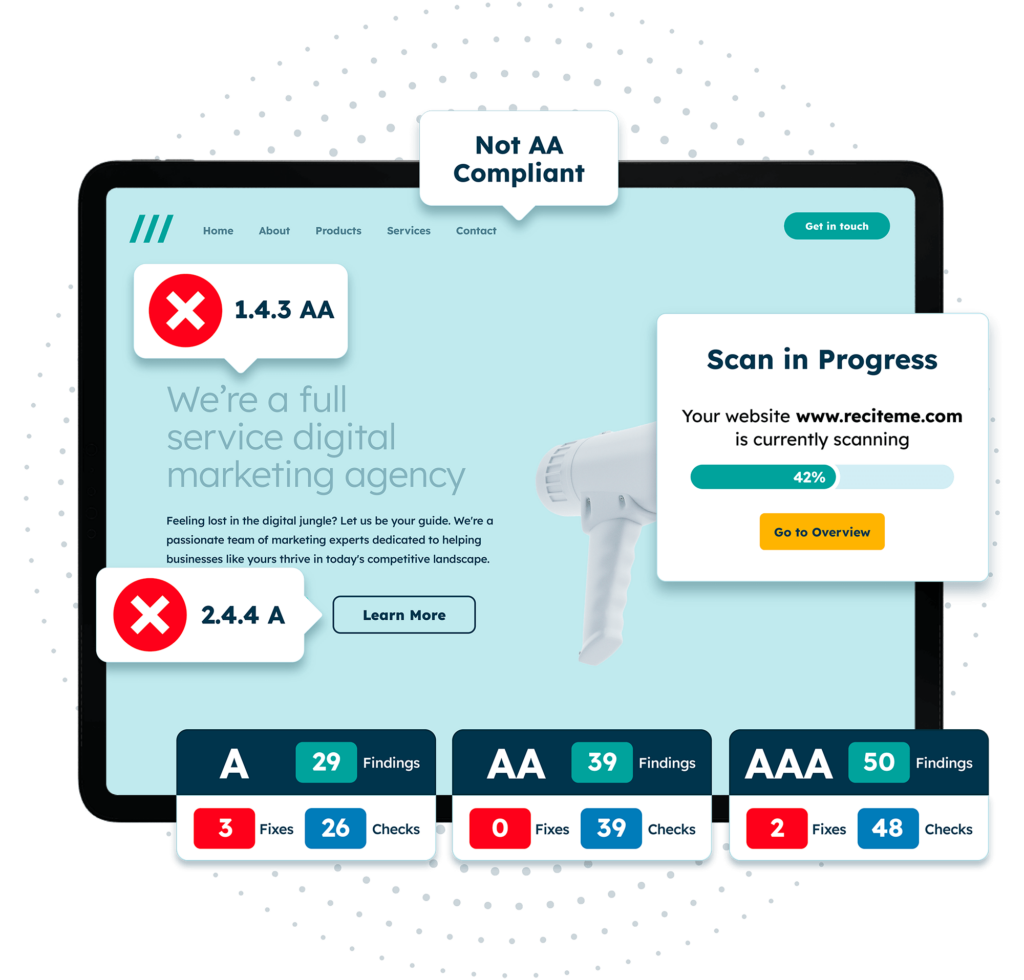
Get a free automated accessibility check of your websites homepage. This will identify and highlight any compliance issues on your website. Followed by recommendations on how to implement the necessary changes to make your website more accessible.
Best practices for accessible SaaS design
Accessibility should be integrated into every stage of the product lifecycle, from initial design concepts to ongoing updates. By following established best practices, SaaS providers can deliver a more inclusive experience for all users.
Keyboard accessibility
Not all users rely on a mouse or touchpad. Many people with motor impairments and even temporary injuries prefer navigating software entirely with a keyboard or assistive devices like switch controls.

To ensure keyboard accessibility, try implementing these basic principles:
- Ensure all interactive elements (buttons, links, menus, forms) are fully operable via keyboard.
- Use the Tab key to navigate through elements in a logical order.
- Use Enter and Space keys to activate controls.
- Avoid “keyboard traps” that prevent users from leaving a widget or dialog box.
- Include a visible focus indicator (outline or highlight) to show the current position.
Screen reader compatibility
Screen readers convert on-screen content into synthesised speech or Braille, making digital platforms usable for people who are blind or have low vision.
To support these tools, SaaS platforms should:
- Use semantic HTML elements (example: <button> instead of <div>) for proper screen reader interpretation.
- Provide descriptive alt text for icons, images, and functional graphics.
- Structure headings in a clear, logical hierarchy for easy navigation.
- Ensure dynamic or live content updates are announced using ARIA live regions.

Colour and contrast
Colour contrast in accessibility ensures text and interface elements are easily distinguishable from their background, helping users with low vision, colour blindness, or visual impairments read and interact with content effectively.

To provide accessible colour contrasts, you can:
- Ensure text meets minimum contrast ratios: 4.5:1 for normal text, 3:1 for large text (WCAG AA standards).
- Avoid using colour alone to convey meaning; combine with text or icons (example: error messages).
- Offer user options like high-contrast themes, dark mode, or adjustable colour schemes.
- Apply colour thoughtfully to improve accessibility for users with low vision, colour blindness, or situational visual limitations.
Forms and data entry
Forms often serve as the gateway to SaaS platforms, whether users are logging in, registering, or submitting data. Poorly designed forms create significant barriers for users with disabilities, making it difficult or even impossible to complete tasks.
When developing accessible website forms, make sure to:
- Label each input field clearly and link it programmatically for screen reader compatibility.
- Arrange form fields in a logical tab order for smooth keyboard navigation.
- Provide ample spacing and touch-friendly input sizes for mobile users and those with motor impairments.
- Ensure auto-suggestions, placeholder text, and inline help remain visible and accessible.

Accessible multimedia
Multimedia elements such as training videos, onboarding tutorials, and webinars are increasingly common in SaaS platforms. But without proper accessibility, these resources can exclude entire user groups, including people who are deaf and hard of hearing.

Accessible multimedia should be created by following these rules:
- Include accurate captions for videos and provide text transcripts for audio content.
- Make video and audio players fully operable via keyboard with clear play, pause, and volume controls.
- Avoid auto-playing content to prevent disruption for assistive technology users.
- Allow users to start, stop, or pause playback at their convenience.
Customisable UI
A SaaS platform with a customisable interface can adapt to a wide range of needs and preferences, enabling users to work in a way that suits them best.
You can include customisable features like:
- Adjustable text size, line spacing, and fonts to improve readability, particularly for users with low vision or dyslexia.
- Light and dark modes to support people with visual impairments or light sensitivity.
- Menus, panels, and toolbars that can be expanded, collapsed, or rearranged so users can focus on the content and features most relevant to their workflow.
- Letting users control interface animations or motion effects to reduce distractions or discomfort.
- Save user settings across sessions so they don’t have to reconfigure the interface every time.

Responsive and Mobile Accessibility
Many users access SaaS platforms on mobile devices, so designing for responsive, mobile-friendly accessibility is essential.

To help build mobile accessibility, consider implementing these steps:
- Design interfaces to be responsive and mobile-friendly, adapting to different screen sizes without losing functionality.
- Ensure text remains readable without pinch-zoom.
- Make touch targets (buttons, form fields) large enough for users with motor impairments.
- Keep mobile navigation simple, with consistent menus and logical tab order.
- Ensure all accessibility features function equally well on mobile as on desktop.
Business benefits for accessible SaaS platforms
Investing in accessibility goes far beyond meeting compliance requirements, it’s a strategic business decision. Accessible SaaS platforms engage more users, enhance overall user experience, lower legal risks, and strengthen brand reputation.
Reduces legal risks and potential fines
Inaccessible software can expose companies to complaints, audits, or litigation, which may lead to costly settlements, penalties, or reputational damage. By prioritising accessibility, businesses demonstrate a commitment to inclusivity and compliance best practices, lowering the likelihood of disputes. Proactively addressing accessibility issues helps identify and fix barriers before they become liabilities, protecting both the company and its users.


Boosts brand reputation and customer loyalty
When making purchasing decisions 54% of global consumers consider a company’s social responsibility practices. Platforms that are usable by all, including people with disabilities, demonstrate empathy, innovation, and reliability.
By making accessibility a part of product design, SaaS companies strengthen their brand image. This also encourages positive media coverage and word-of-mouth, reinforcing a reputation for forward-thinking development.
Expands market reach to users with disabilities
Globally, the disability market has $1.9 trillion in annual disposable income, representing a significant untapped market for SaaS providers.
Beyond people with disabilities, accessibility features often help users in situational contexts, such as noisy environments, low-light conditions, or on small mobile devices. By designing inclusively, companies increase their market share by building accessible products that reach more users in diverse situations and geographies.


Improves overall user experience
Accessible design benefits all users, not just those with disabilities. Features such as clear navigation, high-contrast visuals, descriptive labels, and keyboard-friendly controls improve usability for everyone. And a recent study reported that for 75% of online consumers, ease of use is more important than price.
Faster onboarding, more efficient workflows, and reduced frustration translate into higher adoption rates and increased customer satisfaction. By embedding accessibility into the core user experience, SaaS platforms can better serve their customers.
Test the accessibility of your website with a free scan
Ensure your platform meets accessibility standards with our Website Accessibility Checker. This tool scans your site for WCAG compliance, identifying issues like missing alt text, poor colour contrast, and navigation barriers.
The tool lets you view your results on the interactive dashboard that tracks progress and improvements over time. You also get a detailed report with prioritised fixes to help you address the most critical issues first. AI-powered tools can even help fast-track your accessibility compliance, offering quick fixes and developer-ready code snippets for seamless implementation.
Our 40-page Digital Accessibility & Inclusion Toolkit helps businesses break down online barriers and make a real impact. It offers practical advice on all aspects of digital accessibility, from writing an accessibility statement to accessible website tips and inclusive hiring.

Conclusion: Build accessibility compliance for your SaaS website
The future of SaaS belongs to the companies that prioritise accessibility. By following WCAG guidelines, designing inclusively, and testing thoroughly, SaaS companies can create platforms that truly work for everyone.
Now you can see accessibility is not just a compliance requirement, it’s a strategic advantage that drives growth, customer loyalty, and innovation. Accessible SaaS platforms improve usability for all users, helping reduce errors and increase efficiency. You can get started today with a free accessibility scan of your website, or speak to an expert for tailored advice.
Accessibility in SaaS FAQs
Looking for a recap or quick summary? Here are a few of our most frequently asked questions to help you get to grips with the essentials:
What does accessibility mean in SaaS?
It means ensuring SaaS software can be used effectively by all people, including those with disabilities.
Do all SaaS companies need to comply with accessibility laws?
Yes, especially if they serve customers in regions with specific accessibility legislation like the European Accessibility Act or the Americans with Disabilities Act.
What are common accessibility barriers in SaaS?
Common barriers include missing alt text, poor colour contrast, forms without proper labels, missing captions and transcripts from multimedia, and non-customisable interfaces.
How can I test if my SaaS is accessible?
Use automated tools (like our accessibility checker), conduct manual testing, and involve users with disabilities to get real-world feedback.
How can teams ensure ongoing SaaS accessibility?
Integrate accessibility into your product lifecycle, from design to development, QA testing, and updates. You should also ensure continuous testing and accessibility training to help maintain standards.
Check out our Products & Services
Ready to take your first steps towards digital accessibility compliance? Then see how we can support your journey with our accessibility solutions:
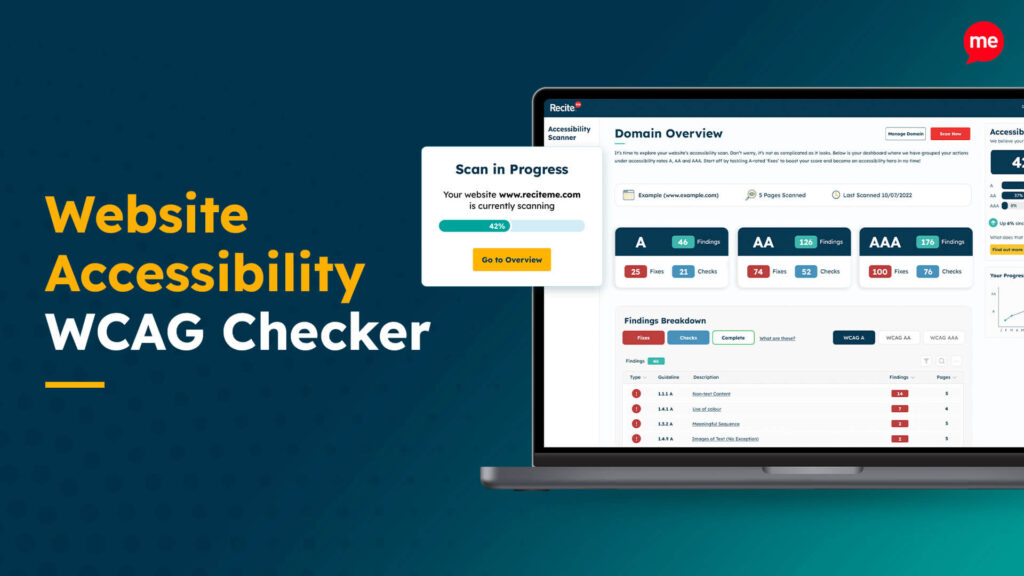
Web Accessibility Checker
Scan, detect, fix, and maintain accessibility compliance standards on your website.
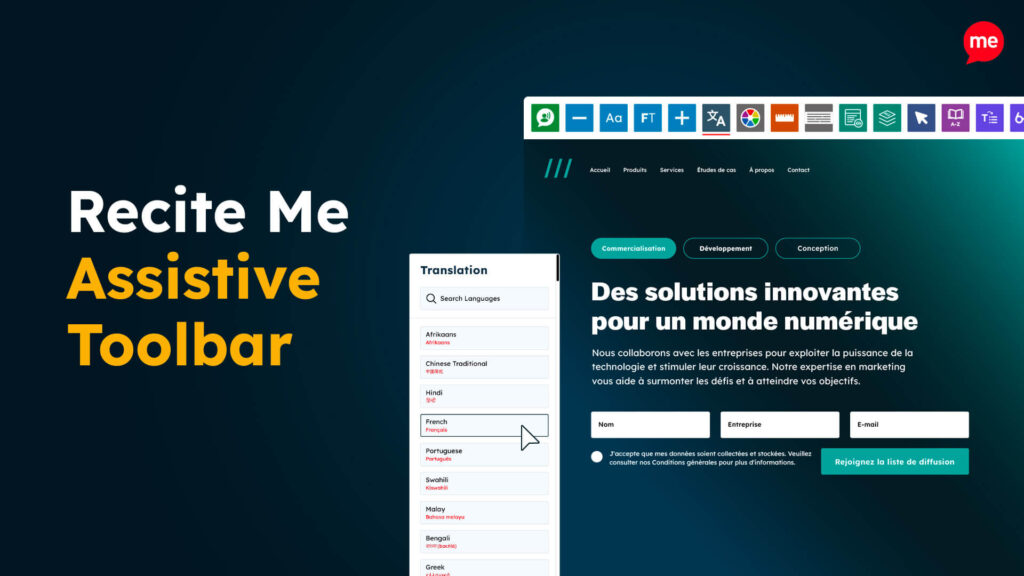
Assistive Toolbar
Make your website an inclusive and customisable experience for people with disabilities.

PDF Accessibility Checker
Check your PDFs are compliant with accessibility standards and run automated fixes.



