Get Your Free Accessibility & Inclusion Toolkit
Download NowIn the digital world we live in, accessibility is no longer a “nice-to-have”, it’s a must. Whether you’re building a website, designing a mobile app, or offering any kind of digital product or service, accessibility should be a foundational part of your strategy.
So, why is accessibility important for both businesses and end users? Let’s explore what accessibility really means, why it matters, and how to implement it in ways that benefit everyone.
What is accessibility?
Accessibility refers to the design and development of digital content, products, and services that can be used by all, including those with disabilities. Accessibility ensures that people can complete tasks with the same ease, efficiency, and independence as those without disabilities. It encompasses a wide range of conditions, such as visual impairments, hearing loss, cognitive challenges, mobility limitations, and temporary disabilities (like a broken arm).

Overall accessibility is about empowering individuals, supporting autonomy, and preventing frustration caused by poor design or implementation.
Why is accessibility important for users and the wider community?
Accessibility affects more people than many businesses realise. Globally, over 1.3 billion people live with some form of disability, according to the World Health Organisation. That’s nearly 1 in 6 people. But the benefits of accessibility reach even further, improving usability for all users, not just those with permanent disabilities.
Accessible design improves usability
Accessible design often leads to better usability overall. For instance, adding captions to videos helps not just those who are deaf or hard of hearing, but also people watching in noisy environments. Similarly, high-contrast text benefits users in bright sunlight and people with low vision alike.
When you design for edge cases, you improve the experience for all users.

Ensures equal access for everyone
Accessibility is about inclusivity. Everyone, regardless of their abilities or circumstances, deserves equal access to information, services, and opportunities. Whether it’s reading a blog post, booking a flight, or applying for a job, accessibility ensures no one is left behind.

Uphold basic human rights
Accessibility is not just a technical requirement, it’s also a moral and ethical responsibility. It supports fundamental human rights, aligning with global efforts like the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD).
By prioritising accessibility, you’re affirming that all individuals have the right to participate equally in society both online and offline.
Accessibility supports aging populations
As populations age, age-related impairments become more common. From reduced vision and hearing to decreased dexterity, older adults often face challenges that accessible design directly addresses. Businesses that invest in accessibility now will be better positioned to serve this growing demographic.
Our 40-page Digital Accessibility & Inclusion Toolkit helps businesses break down online barriers and make a real impact. It offers practical advice on all aspects of digital accessibility, from writing an accessibility statement to accessible website tips and inclusive hiring.

Why is accessibility important for businesses?
Accessibility offers strategic advantages for businesses. From legal protection to enhanced reputation, the ROI of accessibility is real and measurable.
Mitigate legal risks
One of the most pressing reasons to prioritise accessibility is the legal risk of non-compliance. In many regions this can lead to costly legal battles that could lead to additional fines and expensive remediation orders.

Many countries have brought in laws requiring digital accessibility, including:
Companies that ignore accessibility risk facing lawsuits, financial penalties, and serious damage to their reputation. High-profile companies and brands like Domino’s Pizza and Beyoncé’s website have already been taken to Court, highlighting just how critical it is to get accessibility right.
Drive innovation
Designing with accessibility in mind often drives creative problem-solving and innovation.
Consider how:
- Text-to-speech capabilities evolved into mainstream tools like voice assistants.
- Auto-captioning and transcripts now benefit millions in various scenarios
- Keyboard navigation improvements helped create better UX and shortcuts for power users
Accessibility challenges often spark breakthroughs that benefit everyone.

Improve SEO and discoverability online
Search engines and screen readers both rely on well-structured HTML, alt text, semantic headings, and meaningful links. By following accessibility best practices, you’re also improving your SEO which makes your content more discoverable by search engines and users alike.
Accessible content is more indexable, faster to load, and better organised, which Google rewards.

Enhance your brands reputation
Being proactive about accessibility signals a strong commitment to inclusion and social responsibility. It tells your customers and community that your brand cares about everyone.
This positive brand sentiment can translate into stronger customer loyalty, media recognition, and even talent attraction.
Expand your audience and ROI
By making your digital products accessible, you’re unlocking a massive, often underserved market. People with disabilities represent over $1.9 trillion in disposable income globally.
Ignoring accessibility means excluding potential customers, while prioritising it gives your brand a competitive edge in reaching a broader audience.
How to ensure your organisation is delivering accessible products, services, and content online
Not sure where to start? Here’s a practical framework your organisation can follow:
1. Audit your website to identify accessibility issues
Start with a thorough accessibility audit to identify existing barriers and understand how your digital experiences perform for users with disabilities. This includes both automated tools and manual testing, as no single method catches everything.
Key Issues to Look For:
- Missing or incorrect alt text on images
- Inaccessible forms (e.g., unlabeled fields, unclear error messages)
- Low colour contrast between text and backgrounds
- Lack of keyboard navigation support
- Improper use of semantic HTML elements
- Poor heading structure (which impacts screen reader navigation)
Document your findings and rank issues by severity and user impact to guide your next steps.

2. Implement fixes in-line with the findings
Once issues are identified, create an action plan to address them, beginning with the most critical barriers to access. Fixes should be handled collaboratively between developers, designers, and content creators.

Common accessibility fixes include:
- Add alt text that is concise, descriptive, and appropriate for the image’s purpose.
- Improve colour contrast to meet at least WCAG AA standards (4.5:1 for body text).
- Use semantic HTML (e.g. <H1> to <H6> tags for headings, <button> for actions) to ensure assistive technologies understand your page structure.
- Make forms accessible by labeling all input fields, using appropriate ARIA roles elements and providing clear instructions and error messages
- Ensure all functionality is keyboard accessible, including interactive components like dropdowns, sliders, modals, and navigation menus.
- Provide captions and transcripts for video/audio content.
- Allow users to pause or stop moving content, such as carousels or animations.
Additionally, make sure you use version control, staging environments, and code reviews to manage and validate accessibility improvements before pushing to production.
3. Schedule ongoing maintenance to ensure long-term accessibility
Accessibility isn’t something you can fix once and forget. As your site or application evolves with new content, design updates, or third-party integrations, accessibility must remain top of mind.
Build accessibility into ongoing processes:
- Schedule regular audits: Perform accessibility checks quarterly or with each major release.
- Monitor content updates: Train editors and contributors to check accessibility as they publish new material.
- Run user feedback loops: Invite people with disabilities to test new features or provide feedback on user experience.
- Integrate into DevOps: Add accessibility checks into your CI/CD pipeline.
- Stay updated: Monitor changes to WCAG, legislation, and assistive technology trends to keep your practices current.
A proactive maintenance routine helps ensure accessibility doesn’t diminish over time.

4. Train your staff and contributors on accessible design
Training staff and contributors in accessible design ensures that inclusive practices become an integral part of every stage of website development. By equipping teams with the knowledge and skills to apply WCAG guidelines, create clear content structure, use semantic HTML, and consider diverse user needs, organisations reduce the risk of unintentional barriers.

Furthermore, regular accessibility training fosters consistency across design, copywriting, and multimedia production, empowering contributors to identify and correct accessibility issues early. Additionally, ongoing education keeps teams current with evolving standards and technologies, promoting a culture of continuous improvement and demonstrating a genuine commitment to digital inclusion for all users globally.
Real world examples of where accessibility has provided benefits
Accessible websites are vital to people with disabilities and there are thousands of examples to find. Here are some of the best:
Dublin City University
Dublin City University (DCU), serving over 20,000 students, partnered with Recite Me in 2021 to enhance digital inclusion and meet EU accessibility regulations. By integrating the Recite Me Assistive Toolbar, offering features like text‑to‑speech, customisable styling, and translation into 100+ languages, DCU empowered learners to access web content in ways that suit their needs. In a 12‑month period, the tool supported 25,804 unique users across 102,009 page views, with users averaging nearly 4 pages per session.

Humberside Fire & Rescue
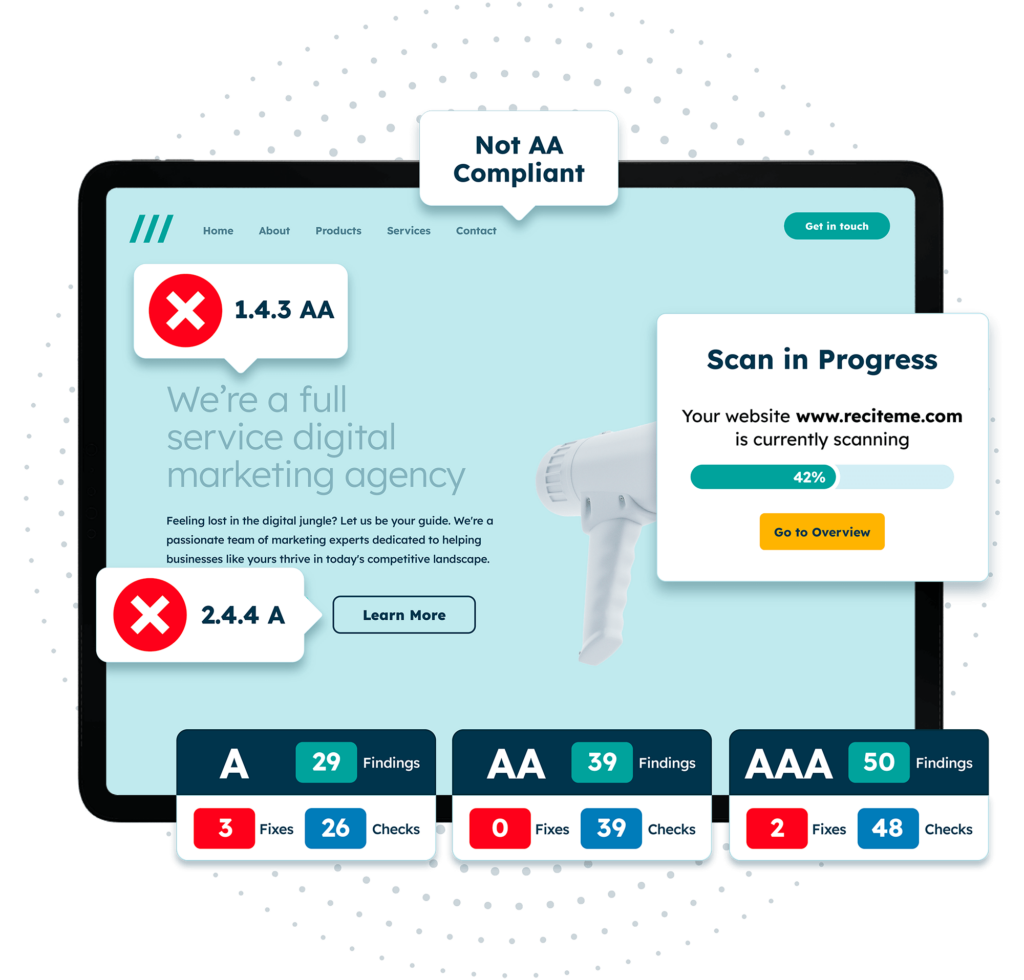
In 2023, Humberside Fire & Rescue Service enhanced its website accessibility by implementing the Recite Me Accessibility Checker. Serving nearly one million people in Northern England, the organization uses the tool to scan content, flag key issues, and prioritize fixes through an accessibility queue. Integrated into daily workflows, it supports compliance with accessibility standards and reinforces their commitment to inclusion.
Communications Supervisor Ros Barbour praised the Checker as “a game-changer” for its ease of use and guidance in meeting legal obligations.
Get a free automated accessibility check of your websites homepage. This will identify and highlight any compliance issues on your website. Followed by recommendations on how to implement the necessary changes to make your website more accessible.
Conclusion: Don’t wait to implement accessibility
Accessibility is no longer optional, it’s essential. From empowering users to unlocking new markets and protecting your business from legal risks, accessible design offers a compelling blend of ethical responsibility and business advantage.
Making your products and services accessible ensures everyone regardless of ability has equal opportunity to engage with what you offer. And in doing so, you build a stronger, smarter, more inclusive brand.
Start with an audit, make accessibility a part of your design process, and commit to continuous improvement. The results will speak for themselves.
Why is accessibility important FAQs
Looking for a recap or quick summary? Here are a few of our most frequently asked questions to help you get to grips with the essentials:
What does digital accessibility mean?
Digital accessibility refers to designing and developing websites, apps, and content that can be used by people with a wide range of abilities, including those who rely on assistive technologies.
Is mobile accessibility different from desktop accessibility?
While the core principles are the same, mobile accessibility introduces specific considerations, e.g. touch targets must be large enough and spaced out, and content should reformat properly for smaller screens.
What is WCAG, and which level should my website meet?
WCAG stands for Web Content Accessibility Guidelines, the global standard for digital accessibility. It has three compliance levels: Level A (minimum), Level AA (industry standard), Level AAA (highest and most strict). Most organisations aim for Level AA.
Is it too late to fix accessibility if my website is already live?
No, it’s never too late. Start by auditing your site, prioritising critical accessibility barriers, and start making incremental improvements. Even small changes (like improving contrast or adding alt text) can make a meaningful difference.
How often should I test for accessibility?
Accessibility should be tested regularly for existing platforms, during initial development, before major launches or redesigns, and whenever new features or content are added.
Check out our Products & Services
Ready to take your first steps towards digital accessibility compliance? Then see how we can support your journey with our accessibility solutions:
Web Accessibility Checker
Scan, detect, fix, and maintain accessibility compliance standards on your website.
Assistive Toolbar
Make your website an inclusive and customisable experience for people with disabilities.

PDF Accessibility Checker
Check your PDFs are compliant with accessibility standards and run automated fixes.



