Around 1 in every 5 internet users have a disability that makes accessing online content difficult. So it’s common practice and highly recommended for businesses to include an accessibility statement on their website.
But what exactly is an accessibility statement? What information do you need to include? How do you write one? And where should it be on your website? Read on to find out as we guide you through the process and show you exactly how to write an accessibility statement.
What is an Accessibility Statement?
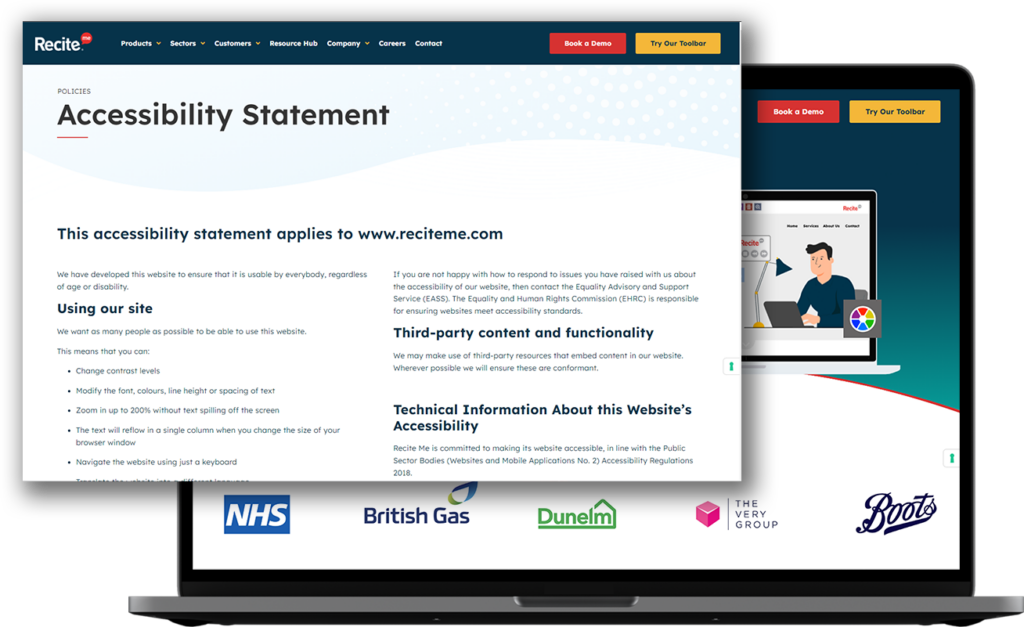
A web accessibility statement for your website is an important information page that clearly states the level of web accessibility to which the website aims to conform. Often, accessibility statements and help pages are bundled together, but it is advisable to have a whole page dedicated to your web accessibility statement.
Is an Accessibility Statement Required?
No, currently an Accessibility Statement is not a legal requirement. There is no specific law that requires websites or business owners to operate with an Accessibility Statement. However, that does not mean you shouldn’t have one, there are a vast number of benefits to both your business and your customers from having one.

Generate your Free Website Accessibility Statement
At Recite Me we are dedicated to helping businesses around the world become more accessible. One of the many ways in which you can help provide awareness around your websites accessibility is by providing an accessibility statement on your website. You can generate and download one for free with Recite Me at the link below.
Why Provide an Accessibility Statement?
An accessibility statement signals to website visitors that your business is dedicated to providing equal access to information for everyone. Nobody wants to feel excluded or be treated differently. By building an accessibility statement, you demonstrate to those with disabilities that you see them as valuable website visitors.
Accessibility statements also demonstrate an organisation’s commitment to:
Accessibility Laws
There are several laws and guidelines that stipulate how content should be made accessible so that disabled users are not disadvantaged or discriminated against. There are a few variations in rules for public sector companies versus private entities, and it is each individual organisation’s responsibility to check they comply with:
International Laws – examples include The Equality Act (UK), The European Accessibility Act (Europe), The Disability Discrimination Act (AUS), and The Americans with Disabilities Act (USA).
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) Level AA – WCAG AA compliance is legally required for certain websites, and this is the level typically referred to when discussing ‘making a website accessible’.
Brand Reputation
Many modern-day consumers actively look for honesty and transparency in the businesses they frequent. So by openly relaying internal policies and accessibility goals to the public and outlining how you intend to achieve them, you stand to improve your brand reputation.
Continual Improvement
Accessibility statements encourage website users to alert the site owners if and when content is inaccessible to them. This allows organisations to identify areas of their website that are not within current accessibility targets, and make plans to resolve those issues.
What to Include when Building an Accessibility Statement?
An accessibility statement should include information on the functionality of your website relating to its accessibility, but also make reference to any known limitation. Keep this in simple and understandable terms, make reference to exactly what it is that is inaccessible rather than the specific WCAG level. For example it is better to say “text can not be resized” as opposed to “Success Criterion 1.4.4 was not met”
The level of web accessibility your website currently provides.
A description of additional accessibility tools that are available.
Any known limitations or areas of the website that are inaccessible.
Contact information for reporting accessibility difficulties
Future accessibility goals and developments
How to Write an Accessibility Statement
Most accessibility statements begin with a short intro, expressing an open commitment to providing an accessible website. From there, you simply work through the points listed above, providing the relevant details for each section. Your accessibility statement needn’t be lengthy, so as long as all of these points are covered, you should be on track.
There are, however, some other factors to bear in mind:
Language
Give the page a clear and relevant title.
Use simple language that makes your explanations clear.
If you need to use abbreviations, give a complete definition the first time you use them.
Structure
Use headings properly – an H1 tag should only be used for the title, and H2 – H6 tags for all further headings and subheadings.
Keep sentences and paragraphs short.
Use bullet points or numbered subheadings to break up sections of bulky text.
Ensure text is aligned to the left.
Provide full descriptions in the copy rather than using any footnotes.
Format
Give all links discernable names.
Use dyslexia-friendly fonts – i.e. sans serif accessibility fonts like Arial or Helvetica.
Use a minimum text size of 12.
Provide alt text for all images.
Avoid blocks of capitals or italic text.
Publish in HTML format.
Only use underlining for links.
Accessibility Statement Template Generator
Writing an accessibility statement by yourself for the first time can be a significant challenge. Need some help getting started? You can access the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) free web accessibility statement generator here.
Generate your Free Website Accessibility Statement
At Recite Me we are dedicated to helping businesses around the world become more accessible. One of the many ways in which you can help provide awareness around your websites accessibility is by providing an accessibility statement on your website. You can generate and download one for free with Recite Me at the link below.

Where to Place Your Accessibility Policy Statement
Many companies hide their accessibility statements away in a difficult to find location on their website, but this is not recommended. Visibility is vital, so your accessibility policy statement should be included on the footer of every page alongside the links to your privacy policy, security policy, and terms of service etc. This way it is easily accessible, no matter what page of your website visitors land on. Below you can see some of the key areas to address in creating a accessibility statement template for your initial draft.
What if Your Website Isn’t Accessible Yet?
If you are striving for better online inclusion goals but are not quite there yet, that’s OK. However, we definitely recommend you make adjustments sooner rather than later, and you should still have an accessibility statement on your website. For now, you can simply include:
Your intent and commitment to become accessible – you want your website to be inclusive of everyone, but it’s not yet.
The standards of accessibility you aim to meet in the future – typically explained in relation to WCAG guidelines.
Contact details so people with access needs can reach out for information that is currently inaccessible – phone and email are commonplace, but if you choose to use forms or chat services, do make sure they are accessible versions.
If you want to speed up your journey to accessibility. Then be sure to check out our online accessibility checker and wordpress accessibility plugin today.



