In today’s digitalized world, accessibility isn’t just a matter of convenience. It’s a fundamental right. Inaccessible websites present significant challenges for individuals with disabilities, hindering their ability to access essential information and services online.
At the heart of web accessibility – from a legal standpoint, at least – lies the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). This landmark piece of legislation was originally enacted to protect the rights of individuals with disabilities in the physical world. However, its scope has now expanded to encompass digital platforms, ensuring that individuals with disabilities can fully participate in the digital world.
In this handy guide, we’ll run through everything you need to know about ADA website compliance and provide a checklist for you to follow to ensure your online presence conforms with current-day standards.
What is ADA Compliance?
The digital accessibility standards outlined in the Americans with Disabilities Act ensure that online content is equally accessible to everyone. The goal is to remove online access barriers that prevent people with disabilities from effectively navigating and interacting with websites and other online platforms.
Founded on the principles of inclusivity, non-discrimination, and equal access, the ADA comprises five Titles, three of which three relate specifically to digital accessibility:

- ADA Title I relates to employment discrimination, mandating information regarding recruitment, hiring, promotions, training, job assignments, and termination be accessible to everyone.
- ADA Title II addresses the accessibility of public services, programs, and activities, meaning local governments must make digital information equally available to disabled and non-disabled citizens.
- ADA Title III applies to public-facing businesses, requiring companies to provide full and equal online access to their goods, services, facilities, privileges, advantages, etc.
By adhering to ADA compliance standards and creating ADA compliant web design, organizations demonstrate their commitment to inclusivity and accessibility. By fostering a digital environment that is welcoming and equitable for everyone, regardless of ability.
Stay ahead of the game when it comes to Digital Accessibility laws and compliance in the United States. Learn about all the different federal and state-level regulations, see real examples of web accessibility lawsuits in different regions and discover a 7-step action plan for building accessible websites.

Is ADA Compliance Mandatory?
The short answer: Yes. And not just because it’s the right thing to do.
While Title II relates specifically to public sector offices and agencies, Titles I and III also apply to private and public-facing organizations, regardless of size or industry. It could be a small eCommerce website or a large multinational brand.
There is still some debate about whether websites should be considered ‘places of public accommodation’ under the ADA. However, recent legal developments have continued to underscore the importance of ADA compliance in the digital realm. The number of digital accessibility lawsuits has been rising exponentially, with courts across the country regularly ruling in favor of plaintiffs in cases alleging ADA violations. Such rulings have established a precedent that websites are indeed considered places of public accommodation and must therefore adhere to ADA standards.

The Role of WCAG in ADA Compliance
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) serve as the cornerstone of ADA compliance efforts, providing a comprehensive set of technical standards and best practices for ensuring web accessibility. Developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), WCAG outlines various principles, guidelines, and success criteria aimed at making digital content more accessible to individuals with disabilities.
WCAGs ‘POUR’ Principles
WCAG encompasses criteria that affect usability, functionality, and overall user experience. The guidelines encourage website owners and developers to design and maintain online properties to ensure content is perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust for all users:
- P = Perceivable: Information must be presented in ways that users can perceive, encompassing various sensory modalities.
- O = Operable: Interface components and navigation must be operable by all users and assistive technologies.
- U = Understandable: Content must be organized logically, using clear language and navigation structures to facilitate comprehension.
- R = Robust: Reliable content interpretation should be possible using a wide range of user agents, including screen readers.
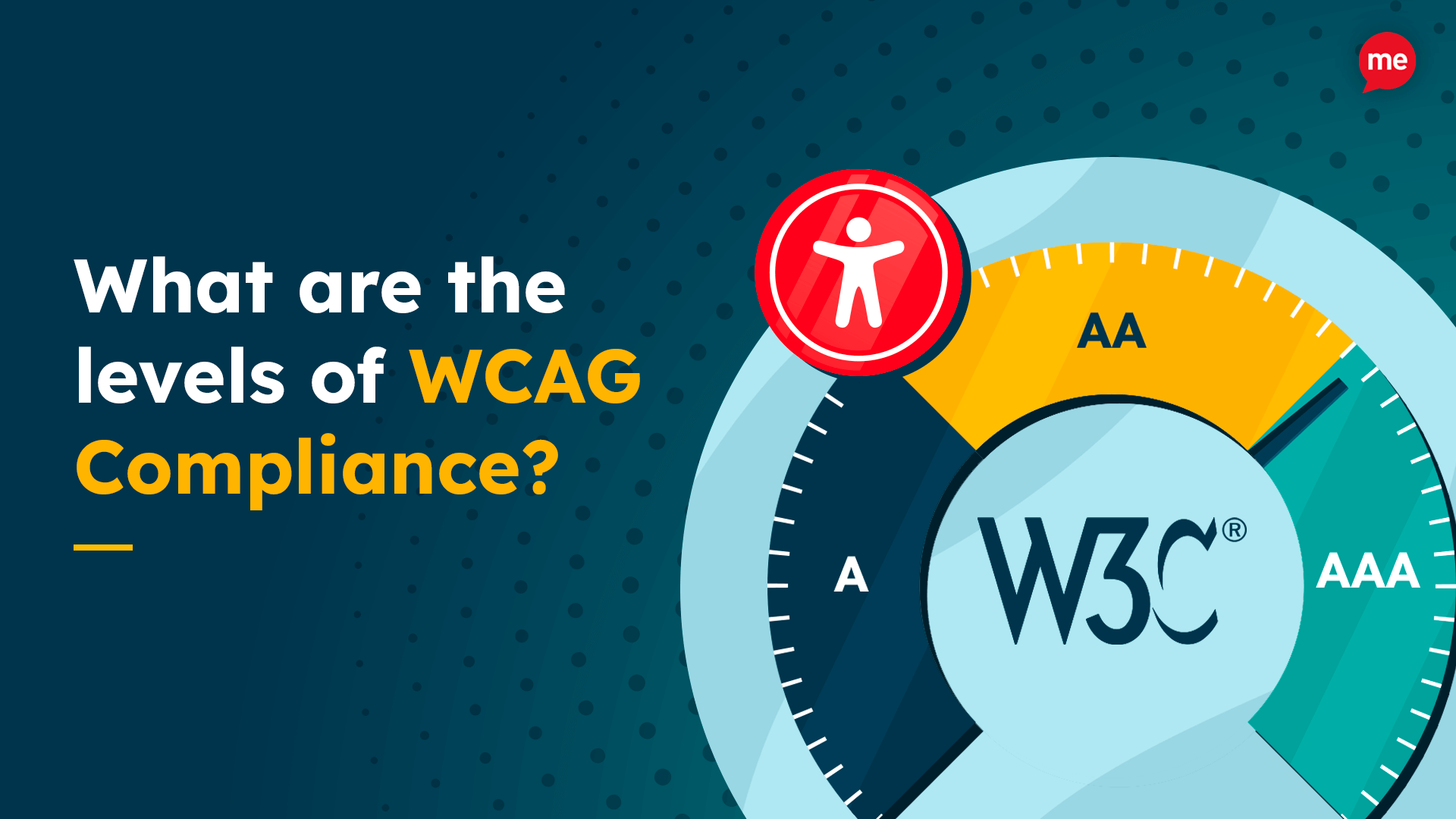
WCAG Compliance Levels
WCAG criteria are organized into different levels of conformance, each indicating the degree of accessibility achieved:
- Level A/ Basic – 30 rudimentary accessibility criteria required to make a website technically accessible.
- Level AA/ Industry Standard – An additional 30 criteria that should be covered to meet an industry-accepted standard of accessibility.
- Level AAA/ Advanced – A total of 78 criteria, which, while desirable, may not be practical or necessary for all websites but represents the highest level of accessibility.
WCAG and the ADA
Most obligations laid out in the ADA (and Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act) mandate WCAG 2.0 Level AA compliance. However, the most up-to-date version is WCAG 2.2, and WCAG 3.0 is on the way soon!
Plus, over 75% of all federal claims now reference WCAG 2.1AA rather than WCAG 2.0 criteria. So, enhanced compliance is recommended to avoid unnecessary legal risk.

Your Comprehensive ADA Compliance Checklist
Achieving ADA website compliance involves addressing various key elements to ensure sufficient accessibility for individuals with disabilities. Here is a comprehensive checklist covering essential components and best practices.
1. Navigation
- Ensure that your website is navigable using keyboard-only navigation.
- Implement skip navigation links to allow users to bypass repetitive navigation elements and access the main content directly.
- Use clear and descriptive labels for hyperlinks and buttons to facilitate navigation for screen reader users.
- Properly label form fields and provide legends to assist users in completing forms efficiently.
2. Content Structure
- Organize content using clear headings and hierarchical structure to facilitate navigation and comprehension.
- Avoid using empty or redundant heading tags that confuse screen reader users.
- Use proper language attributes in the HTML code to accurately identify the language of each page.
- Utilize a dyslexia-friendly font.
3. Text and Media Accessibility
- Provide text alternatives (alt tags) for non-text content such as images, videos, and audio files.
- Ensure that videos have accurate captions and audio descriptions to make them accessible to users with hearing impairments.
- Use descriptive filenames and provide transcripts for audio content to enhance accessibility.
- Ensure website visitors can pause or stop auto-playing audio, or at the very least, be able to control volume.
4. Color and Contrast
- Maintain sufficient color contrast between text and background to ensure readability for users with low vision or color blindness.
- Avoid relying solely on color to convey information. Instead, use other visual cues such as icons or patterns.
- Avoid grey scaling.
- Ensure that interactive elements have sufficient visual indicators to distinguish them from surrounding content.
5. Interactive Elements
- Ensure all website functionality is operable via keyboard, including PDF forms, menus, and interactive elements.
- Provide sufficient time for users to interact with content and avoid time limits on tasks to accommodate users with cognitive or physical disabilities.
- Implement error handling mechanisms to provide clear and concise feedback to users in case of form submission errors.
- Ensure web elements like form fields and checkboxes do not unexpectedly change or jump focus when they receive input.
6. Design and Layout
- Design your website to be responsive and adaptable to different screen sizes and devices.
- Ensure consistent navigation and layout across pages to provide a seamless user experience.
- Avoid using flashing or strobing effects that may trigger seizures or cause discomfort for some users.
- Populate HTML tables with column headers, row identifiers, and cell information.
7. Testing and Validation
- Conduct regular accessibility audits and usability testing to identify and address accessibility barriers.
- Use accessibility checker tools to evaluate your website against WCAG guidelines and identify areas for improvement.
- Engage with users with disabilities through user testing and feedback sessions to gather insights and ensure inclusivity.
- Write and display an easily locatable website accessibility statement (or use a free generator tool) to make your current and future digital accessibility goals transparent and provide avenues for affected individuals to request additional accessibility information.
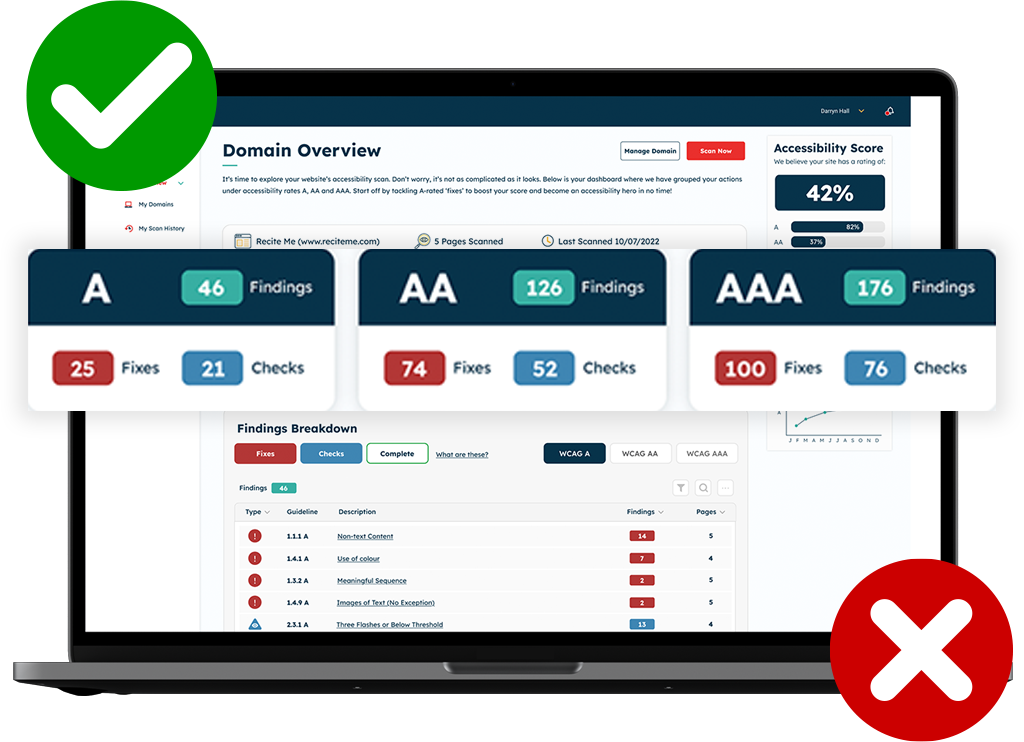
Free ADA Compliance Check of your Website
Detecting ADA Compliance issues has never been easier than it is now. At Recite Me we offer a free automated scan of your websites homepage. This will identify and highlight any non-compliance on your website. Followed by recommendations on how to implement the necessary changes to improve your websites accessibility score and standing.Methods of Meeting ADA Compliance Standards
Ensuring compliance requires a systematic approach of implementing various ADA Compliance Solutions. Here’s a rundown of the most common methods of ensuring ample accessibility. However, do note that there’s no outright winner among any of these strategies, and the most comprehensive approach typically involves a combination of more than one methodology.
Usability Testing
Usability testing involves observing real users with disabilities while they interact with your website to identify accessibility barriers and usability issues. This strategy can provide valuable insights and may uncover issues that automated tools may overlook.
While feedback from real-world user experiences can be effective in helping you prioritize accessibility improvements, usability testing is typically a time-consuming and resource-intensive endeavor. It requires the recruitment of diverse user groups and coordination of testing sessions. Plus, the results may vary depending on the participants’ backgrounds, abilities, and preferences.

Accessibility Checkers
Accessibility checkers are automated tools that scan websites for accessibility issues based on WCAG guidelines. They provide a quick and efficient way to identify common accessibility barriers and prioritize remediation efforts.
For example, the Recite Me Accessibility Checker conducts an exhaustive audit by running 396 separate WCAG-based scans, identifying non-compliance issues, and generating a comprehensive report complete with a prioritized fix queue for effective resolution.
Whichever tools you use, bear in mind that automated testing should always be supplemented with manual evaluation for optimum results. For example, a computer can determine whether an image on a website has an alt-tag attribute or not. However, a human eye is needed to ensure that the alt-tag text accurately describes the image.
3rd-Party Accessibility Auditors
Third-party audits involve hiring external accessibility experts or consulting firms to conduct website evaluations on your behalf. Experienced auditors can provide expert guidance and recommendations for achieving and maintaining ADA compliance. And, should you end up in legal hot water, they can help to demonstrate due diligence in legal proceedings.
The downsides of third-party audits are that they can be costly, especially for large or complex websites, and may require ongoing engagement to address identified issues. Additionally, the availability of qualified auditors may be limited, scheduling may require a significant lead time, and individual auditor interpretations of accessibility guidelines may vary, leading to discrepancies in findings and recommendations.
The Benefits of Developing an ADA-Compliant Website
Creating a compliant website goes beyond just legislative ADA requirements for businesses. It’s about building a digital space that is inclusive and accessible to everyone. Here’s a list of key benefits.
Improving User Experiences
ADA compliance fosters a user-centric universal design approach, resulting in websites that are more navigable, intuitive, and efficient for everyone. So, it’s not just about making accommodations for disabled website visitors. Improving accessibility results in an overall increase in user satisfaction and engagement.
Reaching a Broader Audience
Research shows that one in four Americans has a disability that can make accessing online information challenging, and the annual spending power of the disabled market is estimated to be $13 trillion. So, making your website usable by individuals with disabilities, elderly users, and those using assistive technologies should be a no-brainer.

“At Bossier Parish Libraries, we strive to provide accessibility for all; with an average of 1 in 3 adults in Louisiana navigating the world with a disability, Recite Me helps us do so. Recite Me’s technology can surmount a variety of barriers, such as vision or hearing loss, which allows us to fill our role of serving the needs of the community as a whole, ensuring that all are welcome and included.”
Clara Anne Madison
Staff Development Librarian, Bossier Parish Libraries

Enhancing SEO And Web Visibility
Many accessibility features, such as descriptive alt text for images and well-structured content, also contribute to search engine optimization (SEO). ADA-compliant websites tend to rank higher in search engine results, leading to increased visibility and organic traffic.
Building Brand Reputation and Trust
Demonstrating a commitment to accessibility sends a positive message about your brand’s values and inclusivity. ADA compliant websites are perceived as more trustworthy and reputable, enhancing brand loyalty and fostering positive customer relationships.

“Incorporating Recite Me accessibility tools on our website is essential for the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey as it reflects our commitment to offering an inclusive, world-class experience across all our facilities. This approach ensures that both our physical spaces and digital platforms are accessible, making travel and information retrieval stress-free and easy for individuals of all abilities.”
Jimmy Diaz
Executive Advisor to the Chief Communications Officer, Port Authority of NY/NJ

Risks of Non-compliance
All of the above notwithstanding, it goes without saying that compliance with ADA regulations helps mitigate the risk of legal actions like lawsuits and fines resulting from violations:
- ADA breaches carry fines of $55,000 for the first violation, rising to $110,000 for each subsequent violation.
- The cost of lawsuits can run into millions of dollars once legal fees and settlement sums have been accounted for.
- Companies receiving grants or funding from government entities may have their contracts revoked and be placed under increased regulatory scrutiny moving forward.
However, the risks of a non-compliant website are neither purely legal nor financial. The negative PR effect for any business involved in a filing can be significant. The list of potential repercussions includes:
- Boycotts
- Long-term reputational damage
- Reduced employee morale
- Drop in shareholder confidence
Online Accessibility and Inclusion Toolkit
This year we published our Digital Inclusion Toolkit that was developed to help businesses make a real difference to the lives of the millions of people around the world who encounter online barriers. The 40 page document provides practical advice covering the complete landscape of online accessibility from how to write an accessibility statement to our top tips for providing an inclusive recruitment journey.
Take Action Today to Ensure ADA Compliance
Get started on your website accessibility strategy today by working through these action points:
- Contact our team for more advice about WCAG standards and Disability Discrimination Act best practices.
- Find out more about the Recite Me Web Accessibility Scanner.
- Schedule a free scanner demonstration to learn how our technology can help you.
- Run a free scan of your website for WCAG 2.1 AA compliance.