Get Your Free Education Accessibility Guide
Download NowEducation is now a basic human right provided by developed countries around the world. It’s something that is critical to an individual’s development from early years to adulthood. Helping to provide hard and soft skills that will shape their future, both from a working and career perspective, but also how they integrate into society and help to improve their community.
However, each individual has their own experiences and challenges in any learning environment. As people come from a variety of backgrounds, with different abilities, disabilities, preferences and learning styles. As such, it is important for educators to provide an accessible learning environment for students to thrive in.
What is Accessibility in Education?
Accessibility in education refers to the provision of equal access and opportunities to all students, regardless of their physical, sensory, cognitive, or other disabilities. It ensures that students with disabilities can effectively acquire the same information, engage in the same interactions, and enjoy the same services as their peers without disabilities. The goal is to create an inclusive learning environment where every student can thrive and achieve their full potential.

Decades ago, accessibility would have typically addressed physical features, such as classrooms, laboratories, libraries and other common areas. Ensuring they were designed in a way that made access easy, such as ramps, elevators, disabled parking and more. But now, with the digital world becoming an increasingly larger part of the learning in schools, it offers a more complex way to look at accessibility in schools. With an increasing need for accessibility tools to help aid individuals in accessing websites and online resources.
Which Students require good Accessibility Standards?
Good accessibility standards are essential for a wide range of students, including those with disabilities and those without. While the primary focus of accessibility standards is to ensure equal access and opportunities for students with disabilities, they also benefit other students and contribute to creating a more inclusive and effective learning environment for everyone.
As mentioned, accessibility is crucial for people with disabilities, these disabilities are usually categorized as behavioural, sensory impairment, physical and developmental disabilities. Some of the most common conditions include visual/hearing impairments, autism, dyslexia, dyspraxia, motor disabilities and more.
This can be further broken down into students that are experiencing a non-permanent disability. This could present itself as conditions such as temporary vision loss, broken bones that affect mobility, chronic illnesses and more. While these are only temporary conditions, it’s important that students affected by these disabilities can still access the resources they need to maintain their learning during these difficult periods.

Furthermore, accessibility also affects those who are not classified as disabled. This can reveal itself in many different ways, with a variety of different challenges. Although, one of the most common is for students who are not native speakers of the language they are learning in. This means that context and information can easily be lost or misinterpreted by the student. Other situations could include the need for a student to be out of the country for a prolonged period of time, or unable to commute to the physical educational setting. This can be overcome with the use of remote learning, however, this would be almost entirely online learning, so strong website accessibility would be required.
Download our Accessibility Education Guide
Download our inclusive education guide which looks at why digital barriers are a problem, who needs support, the importance of inclusive education, Recite Me clients, and an overview of our data from the past year.Why is Web Accessibility important?
Accessible web practices are important to both educators and students. When web accessibility is done correctly, the benefits can be significant and wide spanning. Some of these benefits for both audiences can be found below.

Benefits to the Student
- Equal Access to Information: Web accessibility ensures that students with disabilities can access and interact with online content and resources. This allows them to participate fully in online learning activities, access educational materials, and engage with their peers and educators.
- Inclusive Learning Environment: By making online content accessible, web accessibility promotes an inclusive learning environment where all students, regardless of their abilities, can participate, collaborate, and learn together.
- Flexibility and Personalization: Accessibility features, such as text-to-speech tools, screen readers, and alternative text for images, provide students with the flexibility to customize their learning experience based on their individual needs and preferences.
- Enhanced Engagement: Accessible web design and content can enhance student engagement by providing clear navigation, easy-to-understand content, and interactive features that are accessible to everyone, including those with disabilities.
- Improved Academic Performance: Students who have access to accessible online resources and tools may experience improved academic performance due to the ability to access and engage with educational materials more effectively.
- Development of Digital Literacy Skills: By using accessible technologies and tools, students develop essential digital literacy skills, such as navigating online environments, using assistive technologies, and understanding the importance of accessibility in digital content creation and design.
- Promotion of Empathy and Inclusion: Website accessibility initiatives raise awareness and promote empathy and understanding among students about the diverse needs and experiences of individuals with disabilities. This fosters a culture of inclusion and respect within the educational community.
- Preparation for Future Opportunities: As students with disabilities gain access to accessible online resources and develop digital literacy skills, they are better prepared for future educational and employment opportunities in an increasingly digital world.
Benefits to the Educator
- Expanded Reach and Impact: Web accessibility allows educators to reach a broader audience of students, including those with disabilities, ensuring that everyone has equal access to educational materials and resources. This enables educators to make a positive impact on the learning experiences and outcomes of all students.
- Inclusive Teaching Practices: By incorporating website accessibility principles and features into their teaching practices, educators can create inclusive learning environments that accommodate diverse learning needs and preferences. This promotes equity, diversity, and inclusion in education and fosters a sense of belonging among students.
- Professional Growth and Development: Educators who are knowledgeable and skilled in web accessibility principles and practices can enhance their professional growth and development. By staying informed about accessibility standards and incorporating accessible design principles into their teaching strategies, educators can improve their instructional methods, adapt to diverse student needs, and enhance their overall effectiveness as educators.
- Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements: Web accessibility ensures that educational institutions and educators comply with legal and regulatory requirements related to accessibility, such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines). By adhering to accessibility standards and guidelines, educators can mitigate legal risks and ensure that their educational materials and resources are accessible to all students.
- Fostering a Culture of Inclusion and Respect: By prioritising web accessibility in education, educators foster a culture of inclusion, respect, and understanding among students and staff. This creates a positive and supportive learning environment where everyone feels valued, respected, and empowered to succeed.
5 Reasons Why an Accessible Education Website is Essential
An accessible website ensures that students, parents, faculty, and staff of varied backgrounds and personal circumstances can access and engage with educational resources, regardless of individual ability.
1. Adapting to Evolving Technologies
As people learn and the digital landscape evolves, new technologies continue to shape the way people interact with the online world. To provide learners an optimal experience, its imperative that educational providers keep up with the pace of change by providing features like:
- Mobile Accessibility – With the prevalence of smartphones and tablets, educational institutions must ensure their websites are mobile-responsive to different screen sizes and orientations for easy on-the-go access.
- Voice Recognition – Incorporating voice recognition and control into an accessible website allows individuals with mobility impairments to navigate and interact with the content using spoken commands.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Assistants – AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants offer personalized support and information about course registration, finding resources, and can answer frequently asked questions.
2. Catering to Varied Use Scenarios
The educational journey encompasses various stages, each demanding specific online interactions. A well-designed, accessible website should address the following scenarios:
- Pre-enrollment Research – Prospective students, parents, and guardians often explore educational institutions online to evaluate available programs, campus facilities, and admission requirements.
- Enrollment and Course Selection – Once admitted, students often rely on the main website to enroll in courses, access syllabi, and manage academic schedules.
- Post-enrollment Resources – Beyond coursework, an accessible website should provide easy access to academic resources, digital libraries, research materials, and collaborative platforms.

3. Linguistic Diversity
Linguistic diversity is the hallmark of American educational institutions because:
- Over 67 million people in the US speak a language other than English at home (Center for Immigration Studies).
- Between 350 and 430 languages are spoken in the US, making it one of the most linguistically diverse countries in the world (Translators Without Borders).
- 13.7% of all United States residents were born in another country. That’s around 44.8 million people (Congressional Research Service).
- Every year, up to a million students from across the globe travel to America to study, bringing opportunities for education providers to benefit from increased tuition fees and government funding.
4. Inclusive Design for All
It’s estimated that one in four Americans has a disability that can make accessing information online challenging. That may sound like a lot, but it’s essential to remember that up to 96% of disabilities are unseen:
- Visual impairments affect 14 million Americans (National Institutes of Health).
- Learning disabilities affect around 4 million people (Healthy Place).
- Language barriers impact accessibility for the 67 million residents who speak a language other than English (Center for Immigration Studies).
- Hearing loss affects one in eight Americans (National Institute for Deafness and Other Communication Disorders).
5. Legal and Ethical Obligations
Educational institutions have a legal and ethical responsibility to provide equal access to education. Failure by education professionals to comply with the accessibility in education standards can result in lawsuits and tarnished reputations. The two key pieces of web accessibility legislation that apply to education establishments in the US are:
- Title III of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
- Section 508 Amendment to the Rehabilitation Act.
Both exist to ensure website visitors are not discriminated against or treated less favorably online.
Our 40-page Digital Accessibility & Inclusion Toolkit helps businesses break down online barriers and make a real impact. It offers practical advice on all aspects of digital accessibility, from writing an accessibility statement to accessible website tips and inclusive hiring.

What Accessibility Problems Do People Face on School Websites?
Online access barriers occur whenever an element of a website’s design or presentation makes it difficult to read or interact with the content. Users usually struggle for one of four primary reasons:
- Reading Barriers – Including unsuitable font choice, text size, or the color contrast between text and background.
- Comprehension Barriers – The pages don’t flow logically when web copy uses overly complex language or terminology or when alt tags and link descriptions are missing.
- Navigation Barriers – Website errors like empty links and buttons, missing input labels on forms, and missing document language often make keyboard navigation impossible.
- Trust Barriers – Flashing images, videos, or distracting image carousels affect focus and can act as triggers for seizures.

Accessibility Barrier Examples
Let’s look at some real-life examples of access barriers that students could face.
Brayden has dyslexia. He’s researching and comparing engineering college courses but keeps encountering problems. The copy on some websites has poor color contrast with the background, and the justified text and double spacing create a ‘river effect.’ Unable to read all of the course information, he crosses the colleges with hard-to-read websites off his shortlist.
Jeff is a mature student with decreased vision. He’s trying to access his online course syllabus so he can design a study schedule around his job. But, many essential diagrams and images don’t have proper alt text descriptions, so he misses out on crucial information and ends up behind in his studies within the very first month.
Yolena has a shoulder injury and relies on keyboard navigation. She’s trying to upload her coursework and read feedback from her tutor on her previous assignment. But, the assignment page has a confusing and unordered layout and an overly intricate navigation system, making both tasks impossible. She spends half a day trying to submit her work but ultimately ends up having to email her tutor for an extension.
5 Tips for Building Accessible Educational Services
Designing educational services and learning materials with accessibility in mind can be challenging, especially if you have a limited amount of experience or exposure to best practices. Below you can find 5 of our top tips to enhance accessibility in education.

#1 Student Feedback
The students are the beating heart of every educational institution around the world and their opinion matters. Collecting student feedback and listening to recommendations should be important for just about every area of education, accessibility is no different. Allowing students to test new assistive technologies can be a great way to get a feeling for if the technology will be beneficial. Additionally, asking students about current accessibility challenges they are facing and how they could be fixed is another great starting point to drive accessibility changes.
Furthermore, surveys and form submission can be used to collect data on mass, about the performance of software, tools, resources and learning materials. Allowing educators to get an overview of what is and isn’t working well for their students.

#2 Leverage Translation Tools
Approximately 13% of the world’s population speak the English language, with only 5% of the population speaking English natively. This represents a huge proportion of the global population who are unable to access information that is written or presented in English without translation tools. Therefore, providing students with the tools to translate resources can provide a significant boost in their ability to absorb information effectively. While also providing confidence in the fact they know the information they are taking in is correct and hasn’t been misinterpreted or misunderstood. Although, in doing this, it is important that the education provider is using reliable translation technology, otherwise the same problems could occur.
#3 Accessibility Formatted Text
One of the easiest ways organizations can start to address accessibility is looking at how their pages are formatted. Look at individual page elements on school websites and digital resources. Ensure headings are correctly formatted (h1, h2, h3, etc.), disability friendly font (Lexend, Arial, etc.), readable font size (16px+), ability to zoom in and out of page, etc. These simple adaptations to how a page is formulated can help to ensure that people experiencing a range of different disabilities are able to access and read the information on the page easily.
You can learn more about Accessible Fonts here or see how dyslexia friendly fonts can benefit your organization.
#4 Incorporate Text to Speech Software
With an estimated 1 billion people worldwide suffering from low vision or blindness, the impact of visual barriers to education can not be under-estimated. One of the best ways to deal with this is through the use of Text-to-speech software. This accessibility solution is used to convert written text into spoken words, an example of Text-to-speech would be a Screen Reader.
While primarily aimed at those with visual impairments, the software can also be leveraged to benefit those with learning difficulties or limited literacy skills. As these individuals may experience significant challenges when reading text for long periods of time or reading advanced text that has been written to a high reading age.
#5 Evaluate the Possibility of Integrating Accessibility Tools
There are thousands of different accessibility tools that can be integrated into a school, college or universities learning environment. With the list continually improving in quality and growing in options. This presents the option for education providers to weigh up the benefits and costs of using different accessibility tools.
The use of student feedback as we previously mentioned will be an important signal as to the need for accessibility tools. A recent study found that 84% of teachers believe it’s impossible to achieve equity in education without accessible learning tools. A further 87% of teachers believe that accessible technology can help teachers better understand and support all of their students. These statistics provide further evidence for the growing demand for accessibility in education.
Finding accessibility issues is now easier than ever. Recite Me offers a free automated scan of your website’s homepage to highlight non-compliance. You’ll get recommendations on how to fix them, helping to improve your accessibility score.
How can Recite Me help Educational Institutions?
Recite Me is one of the leading accessibility providers, helping to make the world a more accessible place online. We have already helped a number of organizations in the education sector to become more accessible and intend to carry on helping many more in the future.

Accessibility Toolbar
The Recite Me Accessibility Toolbar is one of our core products that helps create more inclusive experiences. The Toolbar works for school websites, colleges, universities and more. Functioning as a plugin that integrates seamlessly with your organization’s website. Some of the main features on the Toolbar include:
- Personalize font size, color and type.
- Screen Mask & Ruler tools for reading.
- Download written content as an audio file.
- Text to speech.
- Translation to over 100 languages.
- Customizing PDF documents.
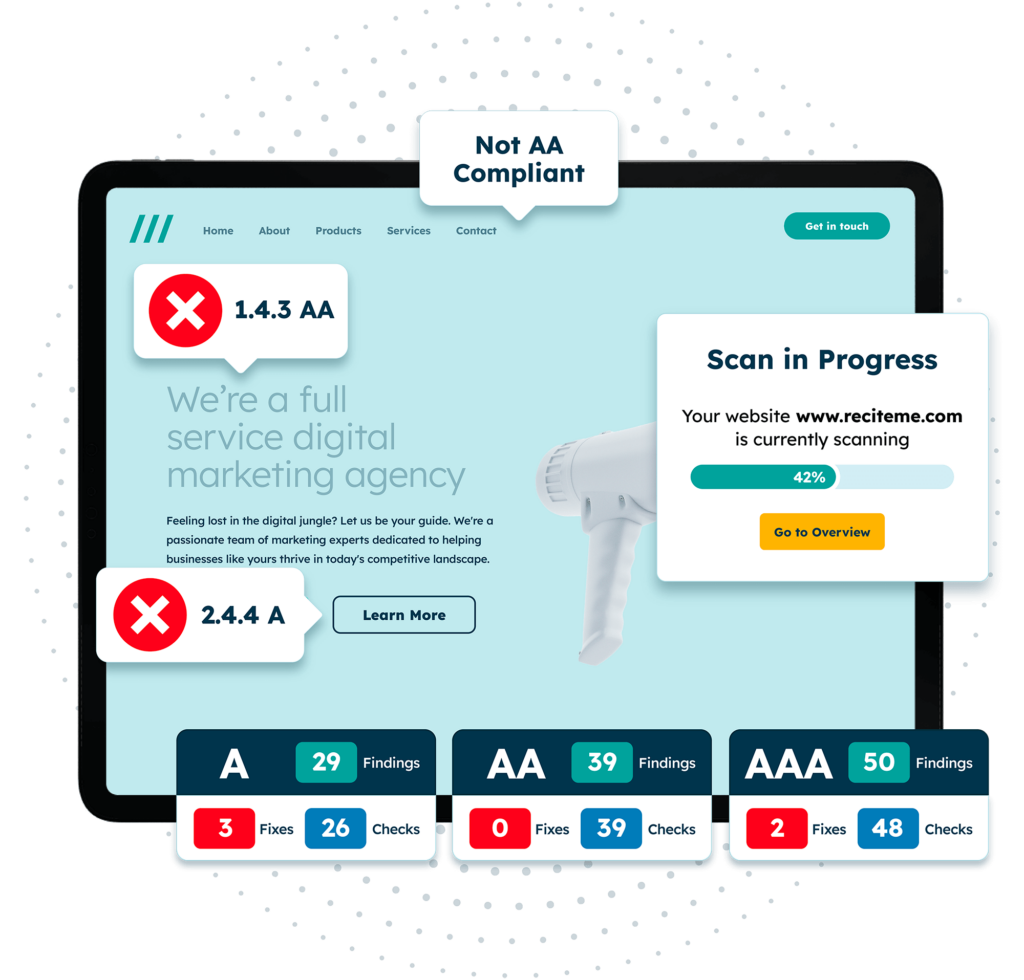
Accessibility Checker
The Recite Me Accessibility Checker is another one of our core products, this one helps to ensure accessible web design. This again works for schools, colleges, universities and any other educational providers website. The checker works by running a scan of your organization’s website and detecting any inaccessible website elements or features. These issues are flagged with clear instructions as to how you can resolve them. The process includes the following:
- Step 1: Scan Your Domains
- Step 2: Identify Accessibility Issues
- Step 3: Fix Accessibility Errors
- Step 4: Track Your Progress
- Step 5: Download & Share and Accessibility Report

You can reach out to one of our team members at Recite Me if you want to learn more about the products or if you just want to learn more about accessibility and how we can help you start your journey towards digital accessibility today!
It’s Time to Get Started Making Your Education Website Accessible!
As 2024 kicks off, government organizations need to plan their budgets. Improving website accessibility should be a crucial consideration! It’s not just about ticking boxes; it’s a legal obligation.
Follow the link below to learn more about how to provide an inclusive education website that comply’s with regulations.





