Get A Free Accessibility Check Of Your Website
Download NowAccessibility remediation is becoming an increasingly critical consideration as organizations globally strive to meet legal web accessibility obligations and create inclusive digital experiences for everyone. But what does it really mean to “remediate” a website for accessibility, and why should your business care?
If your website isn’t already accessibility compliant, the time to act is now! In this guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of accessibility remediation, provide a step-by-step guide to help you get started, and provide information about tools and resources that can help.
What is accessibility remediation?
Accessibility remediation is the process of identifying and fixing issues that prevent people with disabilities from accessing or using your digital content. It involves aligning websites, documents, and multimedia with the relevant accessibility standards. The overarching goal is to remove accessibility barriers and provide equal experience for all users, regardless of ability.
Which standards must you adhere to during web accessibility remediation?
Most pieces of national legislation use the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) as a foundational framework. The guidelines cover accessibility best practices relating to various disabilities, including visual, auditory, cognitive, and motor impairments. However, some legislative compliance frameworks are more outdated than others. This is mainly due to when each specific piece of accessibility legislation was enacted. Here’s a brief overview of WCAG version history and publication dates:
- WCAG 1.0: 1999
- WCAG 2.0: 2008
- WCAG 2.1: 2018
- WCAG 2.2: 2023
- WCAG 3.0: Currently in the drafting process.

Most legislation demands compliance with either WCAG 2.0 or WCAC 2.1 Level AA. However, compliance with the most up-to-date version is always encouraged to avoid unnecessary risk. In addition to WCAG, there are a few other pieces of industry-specific guidance that you should become familiar with:
- ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) Standards: ARIA standards comprise a set of roles and attributes that make web content and web applications more accessible to people with disabilities.
- Mobile Web Best Practices: Although focused on mobile usability, many mobile web best practices overlap with general accessibility principles, ensuring more equitable experiences across various devices.
- PDF/UA (Portable Document Format/Universal Accessibility) Standards: More formally known as ISO 14289, PDF/UA standards refer to a list of requirements for making PDF documents accessible to all users.
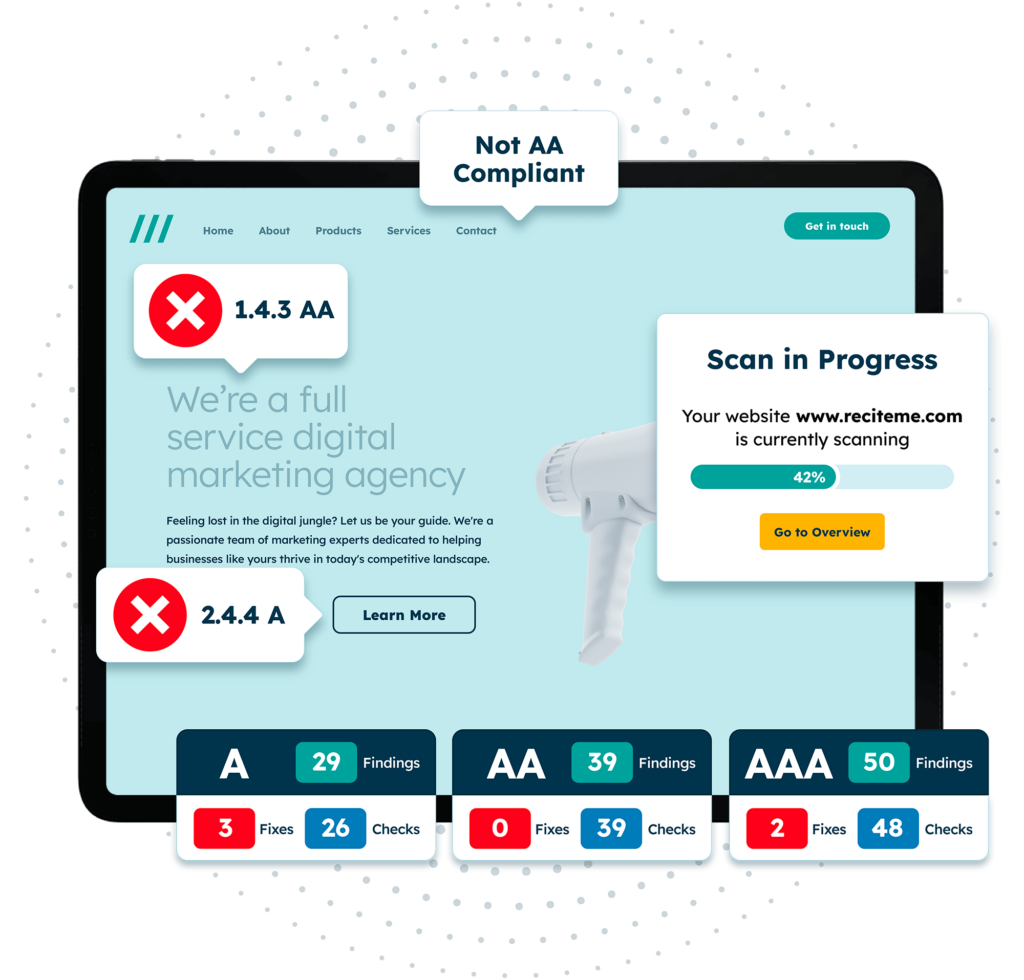
Free Accessibility Check of your Website
Finding accessibility issues is now easier than ever. Recite Me offers a free automated scan of your website’s homepage to highlight non-compliance. You’ll get recommendations on how to fix them, helping to improve your accessibility score.
Your five-step plan for website accessibility remediation
Achieving full accessibility requires a strategic approach. Follow this five-step plan to ensure your accessibility remediation efforts are comprehensive and effective.
Step 1: Audit
Before you can fix any issues, you need to understand where your website stands. Conducting a thorough accessibility audit will help identify areas where your website fails to meet WCAG standards. Typical methodologies include a mix of:
- Automated tools
- Manual testing
- User feedback
Step 2: Prioritize
Not all accessibility issues have the same impact. Your roadmap to accessibility should first focus on fixing the most frequent and severe errors that significantly affect user experience. Examples of issues that should be prioritized include:
- Facilitating keyboard navigation.
- Ensuring all images and multimedia content have alternative text descriptions.
- Providing sufficient color contrast between the text and background.

Step 3: Fix
Address all of the issues identified in your audit in the most logical order. WCAG compliance criteria are separated into three different levels of compliance. So, start with the rudimentary fixes first, then move on to additional and advanced fixes that will further improve accessibility and functionality:
- Level A: Basic – Criteria that should be easy to achieve without much impact on website design or structure.
- Level AA: Industry Standard – The level typically referred to when discussing ‘making a website accessible’ and the level your development team should aim to meet to ensure legal compliance.
- Level AAA: Advanced – The most comprehensive standard of accessibility compliance.
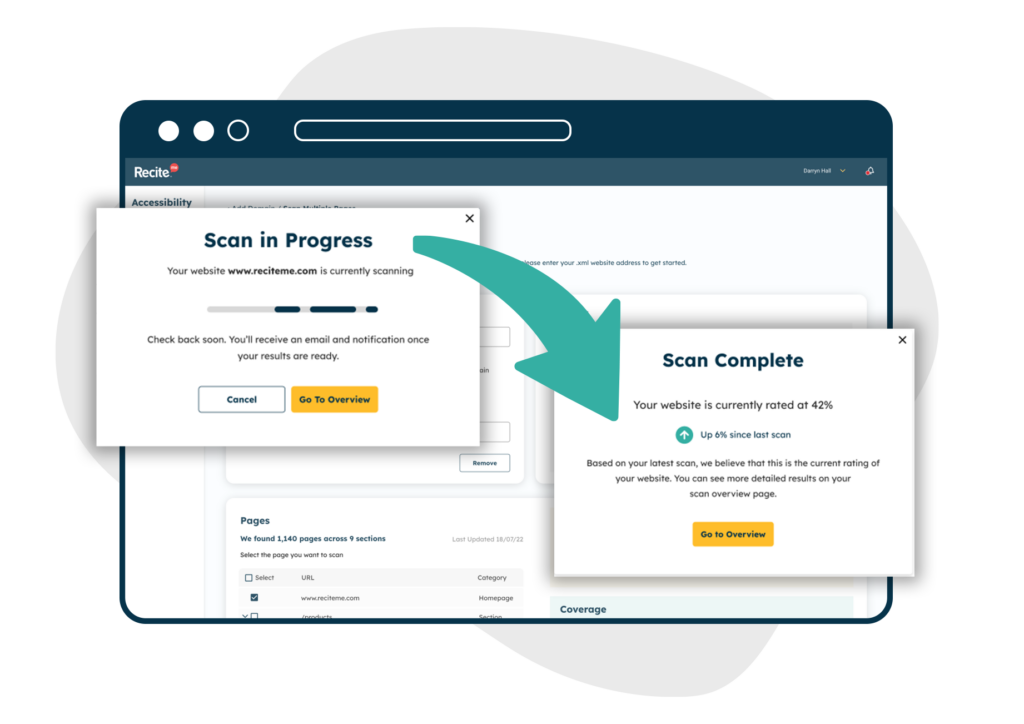
Step 4: Test
Once you’ve made the necessary fixes, you must test your website thoroughly to ensure the accessibility remediation steps you’ve taken have effectively resolved each issue. A combination of the following testing methods will provide the most accurate results:
- Automated testing tools can run lightning-fast checks to identify any remaining compliance violations.
- Manual testing simulates how users with disabilities might interact with your website to verify usability.
- Real-word user testing gives you an insight into additional pain points and barriers that may not otherwise be evident.
Step 5: Verify
Accessibility remediation isn’t a one-time-and-done task. After testing, you must verify that your fixes hold up over time so that accessibility isn’t compromised as your website – and accessibility standards – evolve. Here’s how to do it:
- Ongoing monitoring: Set up automated accessibility checks as part of your website’s regular maintenance routine.
- Accessibility audits: Schedule full accessibility audits periodically, and especially after major updates, redesigns, or feature additions.
- Staff training: Ensure your development and content teams are trained on accessibility best practices to prevent non-compliant features from being reintroduced.
Why accessibility remediation is important
Accessibility remediation isn’t just about compliance. It’s about creating a better user experience for everyone.
 “For people with disabilities, technology makes things possible. For people without disabilities, technology makes things easier.”
“For people with disabilities, technology makes things possible. For people without disabilities, technology makes things easier.”
IBM Training Manual
By removing barriers, you make your content available to a broader audience, foster inclusivity, and demonstrate corporate responsibility.
The Organizational Benefits of Accessibility Remediation
Here’s a list of business-boosting benefits for organizations that act quickly and get ahead of the accessibility remediation curve.
Legal Compliance
Accessible websites are less prone to legal risk. If your site is found to be in breach of web accessibility legislation, potential repercussions can include lawsuits, fines, settlements, and hefty legal costs. The specific criteria you’ll need to meet will depend on where your company is based. However, primary examples include:

Wider Reach and Improved Revenue
On average, one in every six people has a disability that can make accessing online information challenging. That’s 16% of the population! Of that 16%:
- 69% leave a site that they find hard to use.
- 86% would spend more if there were fewer barriers.
- 83% limit their shopping to sites that they know are accessible.
(Source: ClickAway Pound)

Improved Brand Value and PR
Consumers are becoming increasingly conscious in their purchasing decisions. Research shows that 52% of people consider a company’s values when making a purchase, and that rate is even higher among the Millennial and Gen Z generations. In a world where consumers are increasingly value-driven, having an accessible website can do wonders for your reputation—especially in industries where competitors have been slow to catch on!
Enhance SEO
Many recommended best practices for accessibility remediation are heavily weighted on search engine algorithms, helping you attract even more customers. So, the two go hand in hand.
Clair Brotherton, founder of a Clear Bright Web recently told us: “There’s a considerable overlap between features that enhance accessibility and SEO performance. By making your web pages accessible to everyone, you’re also boosting your chances of being found in search.”
Types of Digital Content That May Require Accessibility Remediation
When considering accessibility, it’s essential to look beyond the basics of your website, although ensuring full website accessibility is vital. Here’s a list of other types of content that often require remediation:
- PDFs and Documents: Documents should be structured appropriately for screen readers, meaning all headings and lists should have the appropriate tags.
- Videos: Provide captions and transcripts for videos to make them accessible to people with hearing impairments.
- Forms: Online forms should be easy to navigate and fill out, with clear labels and instructions.
Our 40-page Digital Accessibility & Inclusion Toolkit helps businesses break down online barriers and make a real impact. It offers practical advice on all aspects of digital accessibility, from writing an accessibility statement to accessible website tips and inclusive hiring.

Tools to Help with Your Accessibility Remediation Efforts
Recite Me is able to support businesses of every type in all locations with our innovative suite of on-demand accessibility software tools and resources:

Accessibility Checker
The Recite Me Accessibility Checker scans your domains, running 396 separate WCAG-based scans to identify non-compliance features. The user-friendly dashboard provides an overview of errors and where each is located on your site, then generates a prioritized fix queue for what to tackle first for the best results. You can track your progress in real time using custom reports that help identify and plan your next accessibility remediation actions.
Run a free check or book a demo today!
Assistive Toolbar
The Recite Me Assistive Toolbar allows website visitors to customize pages for ease of navigation and comprehension. Suitable for site visitors with various needs and preferences due to sight loss, cognitive impairments, neurodivergent traits, and physical disabilities, users can:
- Have text read aloud using the built-in screen reader.
- Download and save any written web content as an audio file.
- Choose the exact color contrast between the text and background.
- Change the font type and size.
- Strip away graphics to remove visual distractions.
- Zoom in on any part of a webpage.
- Use the built-in spell-checker and a fully integrated dictionary and thesaurus.
- Access text-to-speech in 65 languages and on-page translation in over 100 languages.
Book a demo today to try it for yourself and learn more.


Website Accessibility Training Course
Recite Me is proud to offer a free introductory course covering best practices and standards for accessibility remediation. The content is comprehensive and covers all the basics regarding:
- The importance of accessibility remediation
- Web accessibility legislation
- WCAG
- Accessibility in the workplace
- Accessible communications
- Accessible documents and processes
- Common accessibility failures and how to avoid them
- Accessibility tools and website testing
Register for free today and get started!



